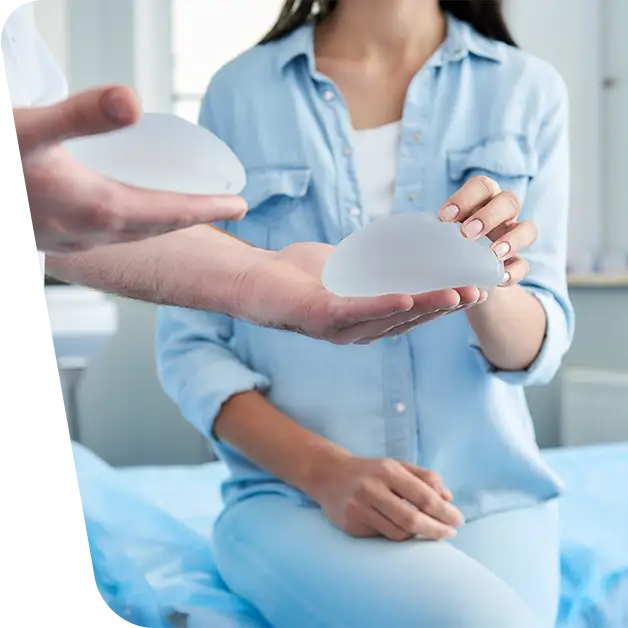
One of the essential procedures in breast cancer treatment is the total or partial removal of one or both breasts (total mastectomy or sectorial excision). This procedure, although necessary, is accompanied by a huge psychological impact on patients, who have their symbol of femininity removed. For this reason, most patients choose to have an operation to restore their self-confidence, called breast reconstruction after mastectomy or sectorial excision. This can be performed sometime after mastectomy, after completion of other adjuvant cancer therapies, or immediately after mastectomy, called immediate breast reconstruction.
Table of contents
ToggleWhat is breast reconstruction?
The main purpose of the procedure is to restore the shape and size of one or both breasts following mastectomy, where all tissue, including the nipple, has been removed to treat or prevent cancer.
Although several factors are involved in determining the most appropriate type of breast reconstruction, there are two main options:
- Implants: This type of surgery uses silicone or saline implants.
- Surgery using your own tissue: This method uses tissue from another part of the body such as the abdomen, back or even the buttocks.
In some cases, the surgeon may use a combination of both techniques to create as natural a reconstruction of the breast or breasts as possible. Additional techniques may help the surgeon reconstruct the nipple and surrounding area if cancer treatment has affected them.
How do we prepare for breast reconstruction surgery?
Preparing for surgery involves, in the first instance, a thorough consultation to assess your health and it is necessary to stop smoking as it can greatly affect the rate of healing and possible complications after surgery.
Which breast reconstruction surgery is right for me?
The type of reconstructive surgery a woman chooses to have after breast excision depends on several factors, including: the size and shape of the breast being reconstructed, the age and health of the woman, her past surgical history, surgical risk factors (e.g. smoking history and obesity), the availability of breast tissue and the location of the tumor in the mammary glands.
Each type of surgery has some advantages and disadvantages, and each woman should consider all the risks and benefits of one when making this decision.
Breast reconstruction with implants
In order for this operation to be possible, there must be enough skin and muscle left after the breast excision to cover the implant. The procedure takes less time than transferring your own tissue and there is less blood loss. Implants also benefit from a shorter recovery period than the other option.
Possible complications of breast reconstruction with implants:
- Risk of infection.
- Formation of hematomas in the reconstructed breast;
- Risk of blood clots.
- Perforation or rupture of the implant, which may leak into the surrounding tissue.
- Formation of hard scar tissue around the implant.
- A possible risk of developing a rare form of cancer that affects the immune system (anaplastic large cell lymphoma).
Obesity, diabetes, smoking and other harmful risk factors can exponentially increase the rate of complications.
You should also be aware of the following. This procedure may not be suitable for people who have previously undergone a radiotherapy plan to treat cancer. Furthermore, implants do not last a lifetime and as time goes by the risk of various complications increases. This is why regular consultations and screenings are recommended for women who have opted for silicone implants to detect possible ‘silent’ rupture.
Breast reconstruction with own tissue
This procedure takes longer than implants and the initial recovery period may be longer.
Complications that may arise include:
- Death of the transferred tissue.
- Blood clots.
- Pain and weakness at the site of tissue removal.
In contrast, using your own tissue can give the breast a more natural and harmonious shape, it can feel softer and more natural to the touch than implants.
Recovery after breast reconstruction surgery after mastectomy
Breast reconstruction surgery is major surgery. Whether you chose implants or used your own tissue, your time in hospital bed can stretch to several days.
You may also need more surgery to completely reconstruct your breast(s).
Both types of surgery make it impossible to carry out most daily activities for up to 2 months. However, the psychological impact of losing one or both breasts may last longer than this.
During the first 2 months of recovery after breast reconstruction surgery, people may experience:
- Fatigue.
- Pain, bruising, swelling or soreness in the breasts and where the surgeon removed tissue during surgery, such as the abdomen, back or buttocks.
- Restricted movement, such as raising your arms above your head.
After breast reconstruction with implants, scarring is reduced and not visible in most cases, but in the other option, scarring also occurs where the donor tissue was removed.
During the initial recovery period, pain relief medication may be prescribed and an elastic bra is recommended to reduce swelling.
The reconstructed breasts will not look exactly like the patient’s natural breasts and will not provide the same level of sensation due to nerve damage at this level. However, with time, some sensation may return.
Today, surgeons specializing in plastic, cosmetic and reconstructive surgery can correct almost any defect, heal scars and delay the effects of ageing. Even more than that, skin surgery is also a fearsome opponent of cancer, helping to cure many types of cancer. Surgeries at the Venart clinic are performed by doctors with extensive experience, specializing in renowned clinics in Europe, the USA and Israel. Find out more in the Plastic, Aesthetic and Reconstructive Surgery section of our clinic.