Table of contents
ToggleWhat are venous stents?
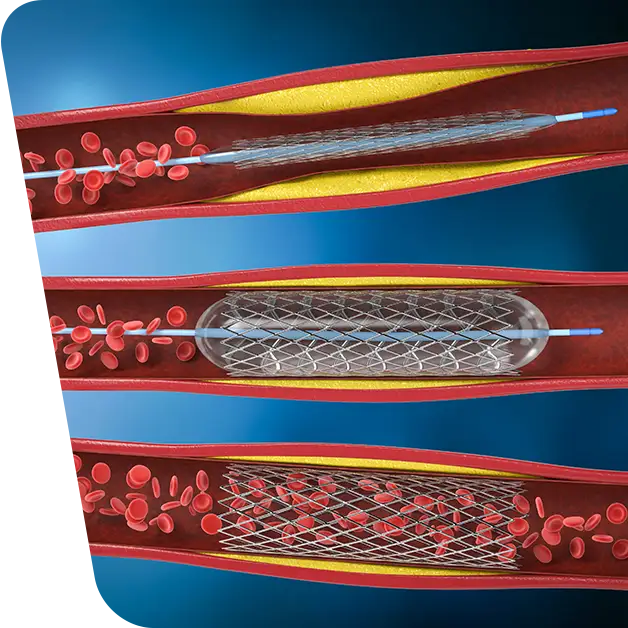
Venous stents are metal mesh tubes that open narrowed or blocked vein walls. They act like scaffolding to keep the veins open. In most cases, surgeons place venous stents in larger, central veins, such as those found in the legs, chest or abdomen.
What conditions are treated with vein stents?
Chronic blood clots or other conditions that compress or narrow veins, restricting blood flow, are the most common health problems for which your doctor may recommend a vein stent.
At VenArt Clinic, our doctors use venous stents to treat conditions such as chronic deep vein thrombosis.
This is a blood clot in one of the large, deep veins that reduces the amount of blood flow flowing through them.
Post-thrombotic syndrome
This syndrome can damage veins. In this case, you may experience problems such as swelling of the affected limbs and chronic pain. If you have suffered from deep vein thrombosis, it may take years to develop symptoms of post-thrombotic syndrome.
May-Thurner syndrome
Because of this condition, the right iliac artery (the artery that connects the abdomen to the right leg) puts pressure on the left iliac vein (the artery that connects the abdomen to the left leg). Because of this pressure, the left iliac artery narrows and becomes scarred, leading to chronic swelling of the left leg, pain and fatigue.
Nutcracker syndrome
This condition causes the arteries near the kidney to compress the left renal vein (the vein that connects to the left kidney), and the blood flows back and causes flank pain (the left side of the abdominal wall between the last rib and the hip) and blood in the urine.
Hemodialysis/arteriovenous fistulas:
If you’re having hemodialysis and the grafts or fistulas are experiencing a decrease in blood flow, your doctor may sometimes recommend venous stents. The stent also opens up the central veins in your chest, which helps with drainage for dialysis access.
How to prepare for the venous stent procedure
Your vascular surgeon will take your medical history, perform a physical exam, and if necessary, may request imaging or other tests, such as an ultrasound, so that your doctor has a clear picture of the structure of your blood vessels to pinpoint any narrowing or blockage. You may also be asked to have a venogram, which is an X-ray that allows your doctor to see the anatomy of your veins.
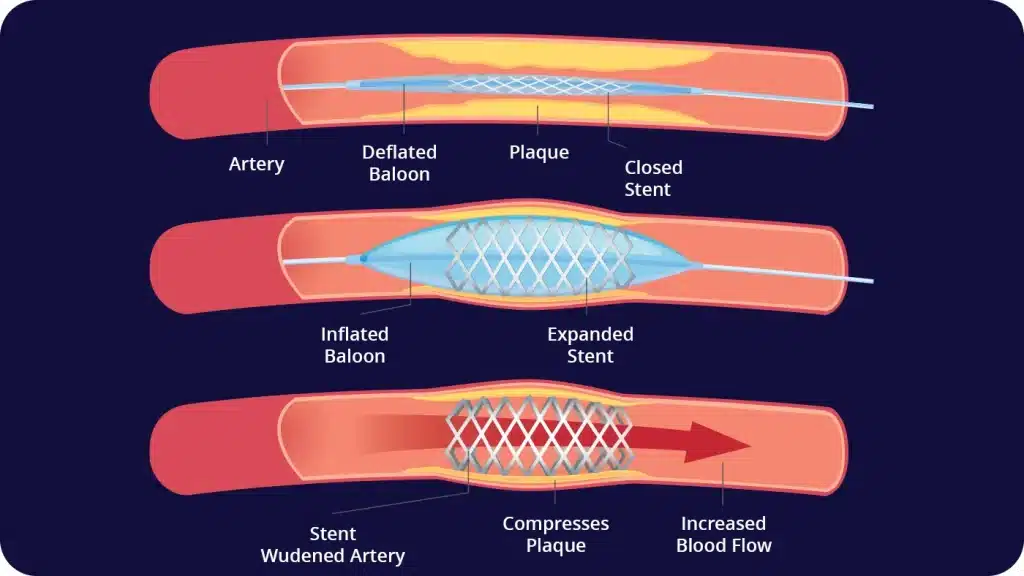
How the venous stent procedure is performed
Moderate sedation is sufficient for your doctor to place the venous stents. However, if he notices a clot or other obstruction in your veins, he may first opt for an angioplasty before placing the stent.
An angioplasty is a minimally invasive medical procedure in which blocked or narrowed veins (or arteries) are widened.
After discussing all the issues, your doctor will perform the following procedures during your venous angioplasty.
He will insert a needle into a vein in your groin area or behind your knee, depending on which vein needs stenting, then insert a guide wire and pass a catheter sheath over it, followed by a guide catheter through the sheath.
After that, the doctor, will use fluoroscopy (x-ray guidance) to direct the catheter to where the vein is narrowed or blocked, and then advance a balloon-tipped catheter to where the vein is narrowed or blocked. That balloon will inflate and deflate it as many times as needed until the vein that has narrowed or blocked widens.
Then, to place the venous stent, your doctor will remove the balloon he used for the angioplasty and insert a catheter with a closed stent on it, which he will place in the vein. The stent will push out the walls of the vein, basically being a support that is meant to keep it open. At the end he will remove the catheter and apply pressure to where he inserted the needle to close the wound.
How long does hospitalization and recovery last after the stenting procedure?
Recovery after angioplasty and stenting is usually short. Discharge from hospital usually takes place 12-24 hours after the catheter is removed. Many patients can return to work within a few days to a week after a procedure.
Why choose VenArt Clinic for a venous stent?
At VenArt Clinic, we are experts in vascular pathology, we can offer you from minimally invasive arterial and venous treatments to the usual classic procedures such as carotid artery surgery , our doctors have decades of experience and specialize in renowned clinics in Europe and the USA.
If venous stenting is not the best option for you, we will recommend other treatments more suited to your needs.
If you would like a consultation, don’t hesitate to contact us.