Table of contents
ToggleOverview
A thoracic aortic aneurysm is an abnormal bulge in the wall of the aorta, which is located in the chest area. This bulge can range from small to very large and if it continues to grow, it can become life threatening. This condition typically develops as a result of chronic high blood pressure, aging, or due to genetics. It can be present for many years without causing any symptoms until it reaches a certain size or ruptures. Symptoms associated with this condition may include chest pain, shortness of breath, coughing up blood and dizziness. If left untreated, a thoracic aortic aneurysm could lead to life-threatening complications such as stroke, rupture of the aneurysm itself or aortic dissection (tearing apart) of the artery wall. Therefore, early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential for managing this condition effectively and preventing serious health risks.
The most common way to diagnose a thoracic aortic aneurysm is through imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scans. These tests will show the size of the aneurysm as well as its location in the chest area. Other tests that may be used include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and angiography (X-ray). Once diagnosed, treatment will depend on various factors including patient’s age and overall health status, size and location of the aneurysm as well as risk factors such as family history or smoking history etc. Generally, medications are prescribed to lower blood pressure and reduce risk while monitoring tests are done regularly to check if there has been any further growth in size of the aneurysm. In some cases surgery may be required depending on how large it has become. Surgical options include open repair where an incision is made in the chest area allowing direct access to repair or replace the damaged section of aorta; endovascular repair which involves placing stents into place through vessels in order to support weakened sections; or hybrid procedures which combine both open surgery and endovascular repair techniques.
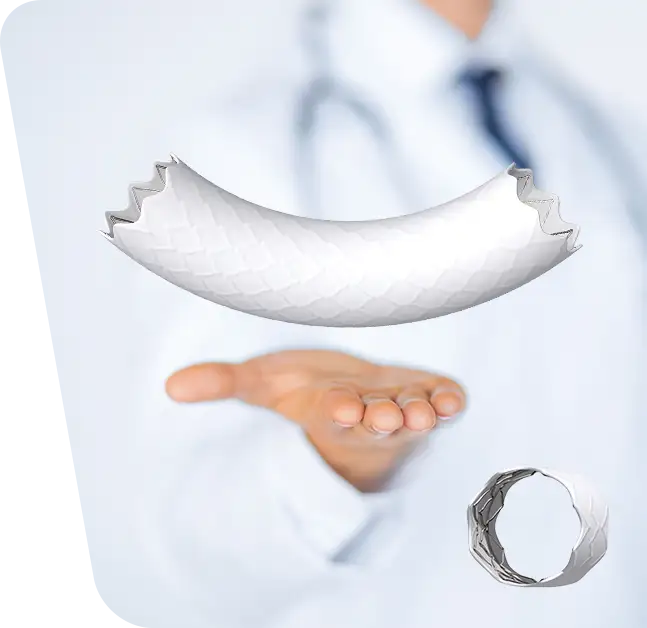
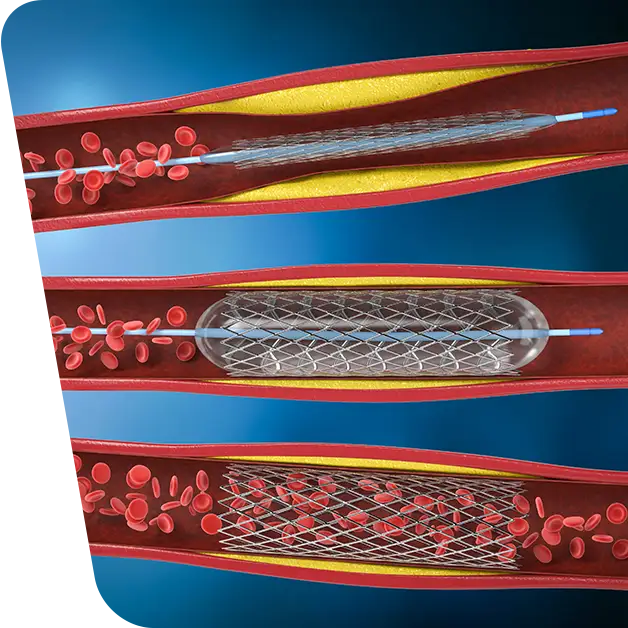
Our surgeons specialize in treating thoracic and thoracoabdominal aneurysms with endovascular stent grafting, a minimally invasive procedure that is safe and effective. The procedure involves the insertion of a fabric tube supported by metal wire stents that is placed into the weakened area of the aorta, sealing it tightly above and below the aneurysm to divert blood flow away from it.
Who is a candidate for an Endovascular Repair of Aortic Aneurysms?
Candidates for this type of treatment must have an aneurysm that has not yet ruptured, and that is greater than 5 centimeters in size; imaging studies can be used to determine eligibility for this procedure.
What is an endovascular stent graft? Procedure details
Endovascular surgery is a minimally invasive procedure involving the use of catheters inserted through small incisions in the groin area in order to gain access to the aorta. During this type of surgery, a stent-graft is deployed at the site of an aneurysm inside the aorta, which helps to prevent blood from pushing on any weak spots or bulges that may be present in this vessel. The stent-graft consists of a fabric tube reinforced with metal wire stents that forms a sleeve around the aneurysm and diverts blood flow away from it. This type of surgery is often chosen over traditional open repair (which requires larger incisions) due to its less invasive nature and shorter recovery time.

Benefits and Risks associated with the procedure
Endovascular surgery can also be used to treat other conditions such as dissection (tearing) of the aorta, pseudoaneurysms, arterial blockages, and trauma to vessels. It can also be used for procedures such as angioplasty, which involves widening blocked arteries; embolization, which is used to cut off blood supply to certain areas; and thrombolysis, which is used to break up clots. The success rates for these procedures vary depending on the type and location of condition being treated, however endovascular surgery typically has high success rates when compared with traditional open repair techniques.
Another major benefit of endovascular surgeries is that they are associated with fewer risks than open repair surgeries. This includes smaller incision sites (which reduce risk of infection and scarring), minimal tissue damage during surgery (due to no need for large cuts), reduced blood loss due to smaller incision sites, faster recovery times (as there are no large cuts or sutures necessary), and less risk for postoperative complications such as discomfort or pain due to minimized tissue damage. Additionally, because these types of surgeries do not require general anesthesia like open repair procedures do, there are fewer risks associated with general anesthesia including adverse reactions and prolonged recovery time.
The risks associated with endovascular repair include:
- leaking around the graft (endoleak)
- movement or migration of the graft
- delayed rupture
- infection
- paralysis
These risks related to this kind of procedure are lower compared with open-chest surgeries due to smaller incisions used during delivery process, as well as shorter recovery times. The benefits also include reduced risk for post-operative complications and improved quality of life due to less pain and shorter hospital stays which can lead to significant cost savings.
Additionally, minimally invasive techniques like endovascular stent grafting can offer excellent long-term outcomes when compared with other similar surgical options such as open repairs or extra-anatomic bypasses. Endovascular repair has proven itself to be highly successful in both elective (i.e., non-emergency) and emergent cases providing patients with improved chances for survival without any major complications or long-term damage. In fact studies have shown positive outcomes even after several years following surgery when compared with other methods.
Recovery and Outlook
How long will it take to recover from endovascular repair of a thoracic anevrysm?
Your hospitalization after the procedure is usually 2 to 3 days. While your recovery will take less time than recovering from open-chest thoracic aneurysm surgery, the early restrictions are similar and include:
- No driving until approved by your physician (usually within 1-2 weeks after the procedure, and no longer taking pain medication)
- No baths until the groin incisions heal; showers and sponge baths around the incision are permitted.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects for approximately 4 – 6 weeks after the procedure.
You will return for a follow-up visit within one month of the procedure. Follow-up imaging tests will take place 1 and 6 months following the procedure to make certain the stent is still functioning.
At VenArt Clinic we provide experienced surgeons who understand how complex thoracic procedures can be; they are knowledgeable about endovascular repair techniques tailored specifically for each individual patient’s needs. Our team works together with other specialized physicians including radiologists, cardiologists & vascular surgeons – all working collaboratively to ensure successful outcome & best possible care for patients undergoing treatments at our clinic. We provide state of the art medical facilities & latest technological advancements enabling us to deliver results remarkable results time & time again.