What are gallstones?
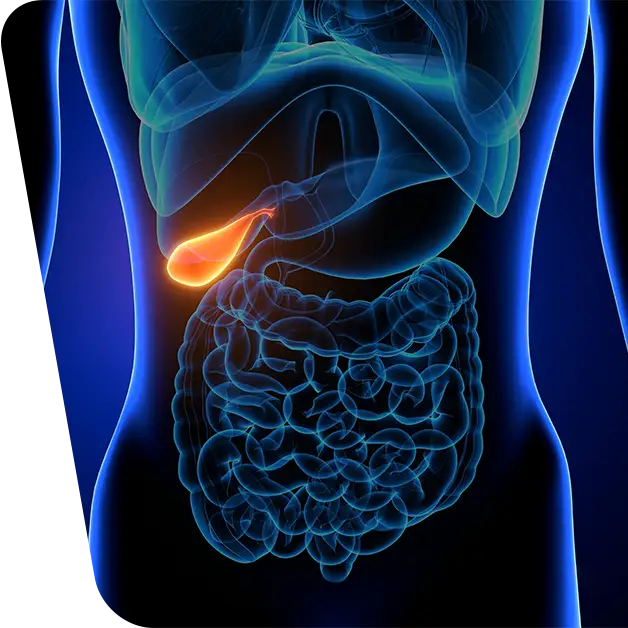
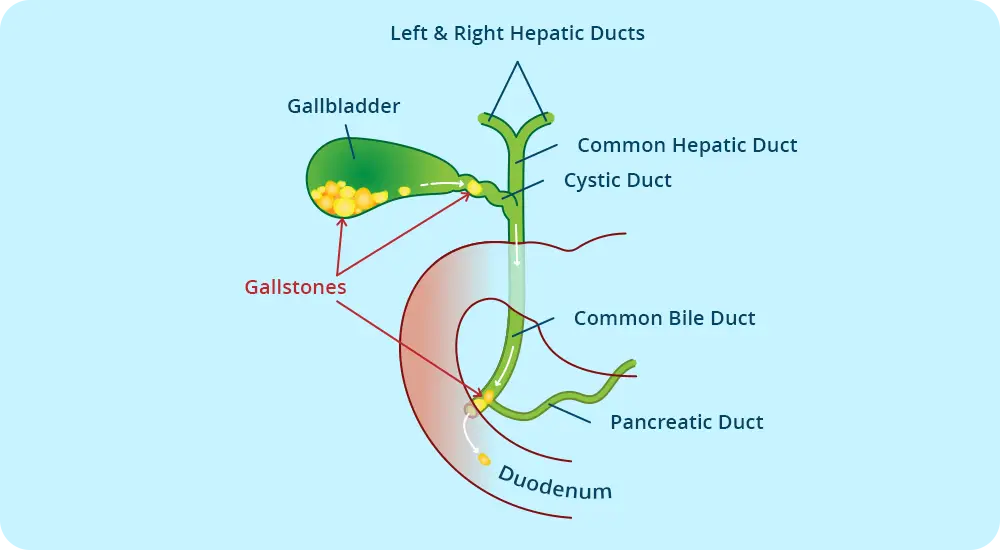
Gallstones are small stones, usually made of cholesterol, that form in the gallbladder. The cholecyst (gallbladder) is a pear-shaped organ located below the liver and is responsible for storing bile and participating in digestion.
According to statistics, 80% of gallstones are cholesterol, the other 20% are bile salts and bilirubin. More details about the gallbladder can be found in the article: frequently asked questions about gallbladder diseases.
Table of contents
ToggleWhat causes gallstones?
Chaotic eating
Leads to long-term storage of bile in the gallbladder; bile becomes hyperconcentrated and stones form.
Excess cholesterol
Both in the diet and in the blood leads to the formation of cholesterol crystals and cholesterol stones.
Obesity, sedentary lifestyle and weight-loss programs
Lead to the appearance of “lazy gallstones” and the long-term storage of gallstones in the gallbladder, with the appearance of bile sediment and stones.
You can find out more about the treatment of obesity through bariatric surgery, also known as obesity surgery, here: What are the benefits of bariatric surgery VIDEO.
What are the symptoms of gallstones?
- Pain – the most common symptom of gallstones – usually occurs after high-fat meals or with certain foods (garlic, cucumber, eggs, coffee, etc.). It is located in the right hypochondrium (under the right rib cage) and epigastrium.
- Nausea, bloating, morning bitter taste, migraines – it is part of the so-called “biliary dyspeptic syndrome”.
- Asymptomatic gallbladder lithiasis – about 70% of patients with gallbladder lithiasis (cholelithiasis) do not show symptoms. This pathology is usually discovered by chance during routine examinations (abdominal ultrasound).
What are the complications of gallstones?
Acute cholecystitis: when a stone blocks the bile duct, inflammation of the gallbladder and infection of the bile occurs.
It is a surgical emergency that occurs in 1 out of 3 patients with gallstones and is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Pain;
- Fever;
- Nausea;
- Vomiting;
- General weakness.
Contact your doctor if after the onset of pain, fever occurs within 1-2 hours.
Acute pancreatitis
The most common cause of acute pancreatitis is gallstones. In the literature it is described as the “great abdominal drama”. It is a complication of the utmost urgency, manifested by intense pain in the upper abdominal floor (abdominal distention), accompanied by nausea, vomiting and marked fatigue.
Mechanical jaundice
Develops when a stone in the gallbladder blocks the main bile duct (choledochus) and is manifested by:
- Jaundice – yellowing of the whites of the eyes (sclera) and skin;
- Brown color of the urine (similar to brown beer);
- Light-colored stools (even white).
If pain, fever and chills are added, it means we are dealing with infection of the main bile duct (cholangitis).
Gallstones diagnosis
The simplest and most effective method of diagnosing gallstones is:
Abdominal ultrasound
It sees the gallbladder and the walls of the gallbladder very well and can also tell us the size of these formations. It can be done as many times as necessary without damaging the body with radiation. Ultrasound is completely harmless to patients and can be performed repeatedly without any long-term negative effects. More details can be found in the Ultrasound section of our website.
Cholangio MRI
When we have some complications, caused by biliary lithiasis, the best method of highlighting gallstones, both in the cholecyst and along the bile duct.
Gallstones treatment
Treatment of gallstones
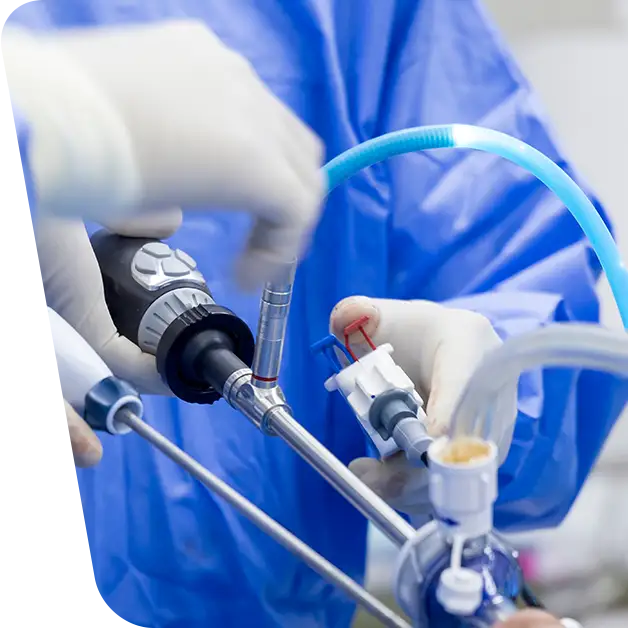
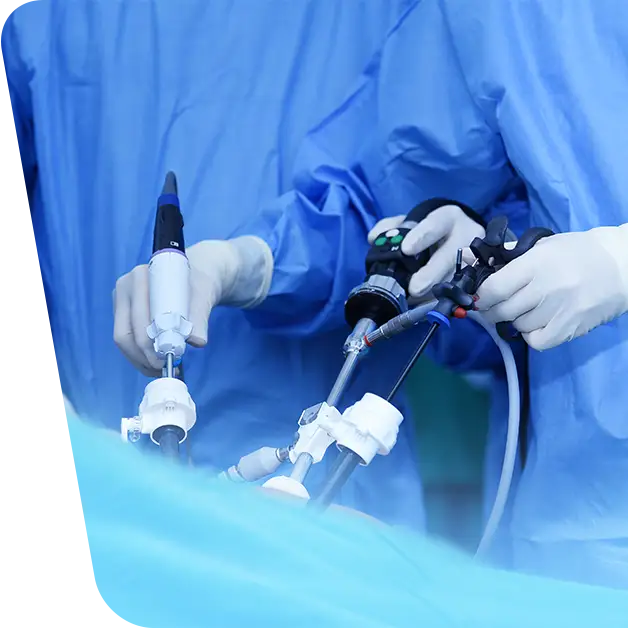
When symptomatic, is always surgical. The operation is always done under general anesthesia and with the help of laparoscopic forceps by removing the gallbladder.
Gallstones treatment
The duration of surgery is from 20 min to 1 hour. The patient is discharged home the day after surgery. Resumption of physical activity is from day 4-5.
Gallstones treatment
Some patients may have softer stools, for up to a week, because the ball is eliminated directly into the intestine. At home you have to follow a food diet for 2-4 weeks. The postoperative check-up is done after one month.
What are gallstones
Gallstones or gallstones are the presence of hardened bile deposits (stones) in the gallbladder or bile ducts.
Among the types of gallstones that form in the gallbladder are cholesterol and pigment stones.
Excess cholesterol and bilirubin are among the causes of gallstones.
Gallstones can be asymptomatic or give symptoms such as severe pain in the upper abdomen.
Among the tests needed to diagnose gallstones are abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, MRI and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
The main treatment for gallstones is surgical and consists of removing the cholecyst. The procedure is performed minimally invasively – laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
Reducing the risk of gallstones
Take the 3 meals of the day
Skipping meals and fasting increase the risk of gallstones.
Gradual skipping
If you need to lose weight, it is good to lose between 0.5 kg and 1 kg per week. Maintain a normal weight. Obesity and overweight increase the risk of developing gallstones.
Reduce the number of calories
Physical activity and calorie reduction help maintain a normal weight. Once achieved, maintain this weight.