What is mastectomy? Mastectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the breast for oncological reasons (breast cancer).
Table of contents
ToggleWhen is mastectomy indicated?
- Breast-conserving operations (sectorectomies) cannot be performed.
- At the request of the patient who chooses mastectomy for personal reasons (instead of breast-conserving operations, which are completed by radiotherapy and screening);
- Patients are at high risk of developing cancer in another breast sector or in the contralateral breast (BRCA 1 and 2 gene mutations). Find out what tests doctors use to identify breast cancer. It is important to remember that screening tests are carried out to detect cancer before the patient shows symptoms.
- When the tumors is large and the breast is small.
How many types of mastectomies are there?
- Modified radical mastectomy – when the mammary gland is removed along with the skin and axillary lymph nodes.
- Subcutaneous mastectomy – when the skin is retained so that the breast can be reconstructed in the same surgical session or over a period of time.
- Nipple-preserving mastectomy – when the breast areola and nipple are preserved for effective breast reconstruction (by muscular or artificial breast implant).
- Bilateral mastectomy – is done in patients with BRCA 1 and 2 gene mutations, at high risk of developing breast cancer. These mastectomies are simple, without lymph node removal and with preservation of the nipple and breast areola.
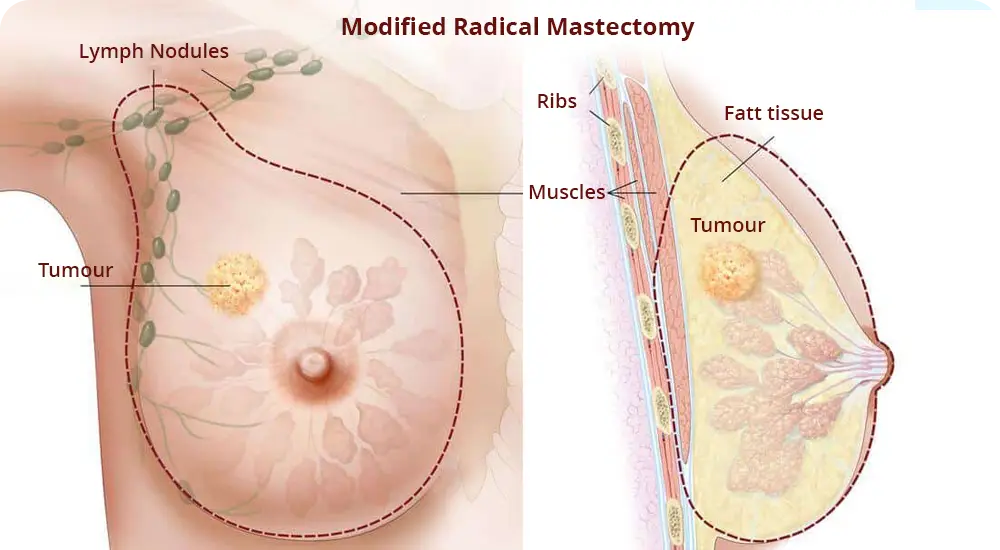
What is mastectomy surgery?
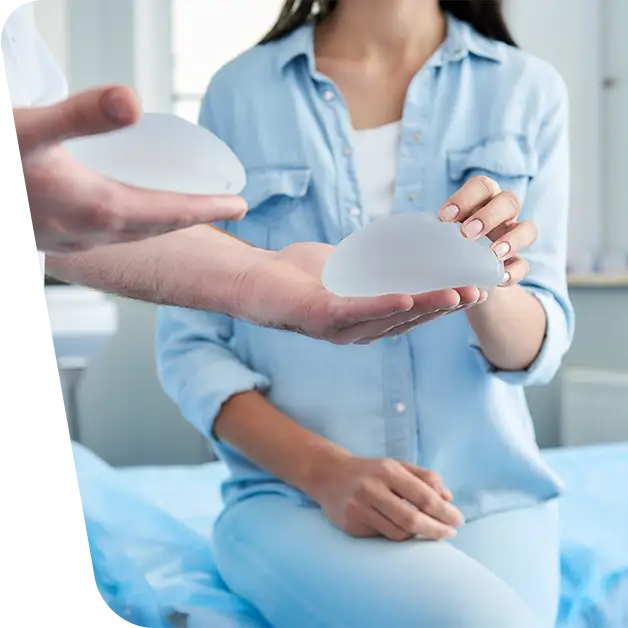
Make an appointment with your surgeon and anesthetist, who will explain what the operation consists of, the reasons for the operation, the anesthesia to be applied, the risks and post-operative recovery. It is also a good time to discuss whether or not breast reconstruction is required, which can be performed in the same operating session or after a period of time.
The types of breast reconstruction are:
- With silicone implant or saline;
- With musculocutaneous flap (when using own tissue);
- A combination of these two methods.
Pre-operative preparation for mastectomy
At your appointment with the surgeon, you will receive instructions on restrictions that are necessary some time before the operation, such as:
- Discontinuation of medications that may influence blood clotting (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or anticoagulants);
- Discontinuation of oral feeding for liquids and solid foods about 8-12 hours before the operation (stomach must be empty during the operation);
- Prepare for a 2-3 day hospitalization period.
How mastectomy surgery is performed
The mastectomy operation is usually performed under general anesthesia and lasts 1-2 hours, depending on the anatomical features of the patient, and when breast reconstruction is chosen, the operation is prolonged up to 6-8 hours.
Usually 1-2 drainage tubes are placed, attached to some collecting bags, to evacuate the scabs from the operative wound, which will be kept for 10-14 days.
After completion of surgery, the patient will be transported to the intensive care unit for cardiopulmonary monitoring.
Discharge after mastectomy surgery
2-3 days after surgery, the patient is discharged with recommendations regarding:
- How to care for the surgical wound (antiseptic solutions to be used, how often the dressing should be changed, how to change or empty the collection bags from the drainage tubes);
- Medication to be administered at home (pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, anticoagulants);
- Physical exercise for recovery (when it is best to start it and with what intensity).
- How to perform personal hygiene (if showering is possible).
- When to wear a bra and whether to use a bra with a breast prosthesis.
What is the treatment after mastectomy surgery?
After the result of the histopathological examination (which takes 1-2 weeks), further treatment may be necessary depending on the stage and histological form of the cancer. This treatment is determined by the oncologist to prevent tumor recurrence or metastases and may include: chemotherapy; radiotherapy or hormone therapy.