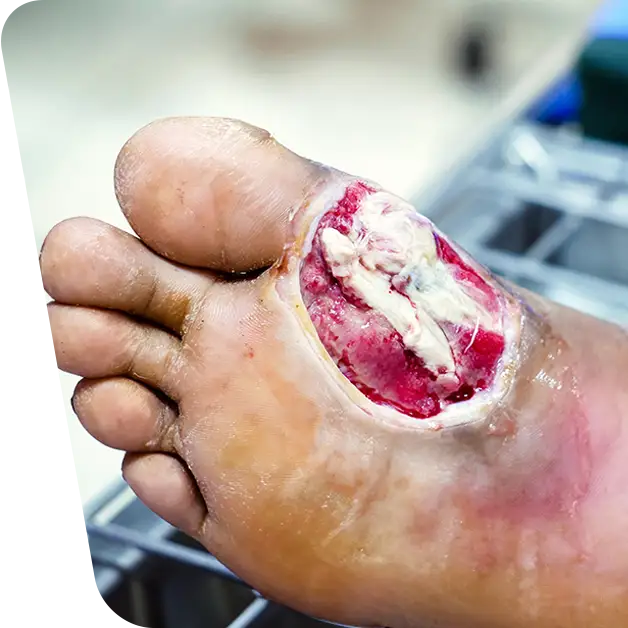
Discolouration of the skin of the legs can hide more than just an aesthetic change; it can often be a sign of blood vessel disease. In this context, an important phenomenon to consider is diabetic foot. It is a serious complication of diabetes and can lead to serious consequences for foot health. In the article below, we will explore in detail what diabetic foot is, identifying the causes and presenting the correct steps to follow and manage this condition in order to prevent severe complications.
Table of contents
ToggleWhat is Diabetic Foot
Diabetic foot is not just a skin problem or uncomfortable sensation. It is a complication of diabetes, a metabolic disease characterised by high blood glucose levels. Nerves and blood vessels in the legs are affected, leading to symptoms such as skin discolouration, swelling, pain and sores that can develop into serious infections. It is essential to understand that the diabetic foot should not be ignored, and prompt treatment can prevent irreversible complications such as foot amputation.
Signs of Diabetic Foot
Diabetic neuropathy: Nerves affected by high glucose levels can cause loss of sensation in the legs, making the lesions often ignored.
Vascular problems: Diabetes affects the blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the feet and promoting sores.
Infections: Unhealed wounds can easily become infected, and the weakened immune system of people with diabetes makes it difficult to fight infections.
Proper treatment of diabetic foot often involves an increased level of complexity, including hybrid surgery, which combines angioplasty procedures with open surgery.

How to Track Diabetic Foot and Prevent Foot Amputation
Blood glucose control: Keeping blood glucose levels under control is key to preventing diabetic foot complications. Regular blood glucose monitoring and treatment adjustment are essential.
- Cause: High blood glucose levels can worsen neuropathy and affect blood circulation, increasing the risk of injury and infection.
- Solution: Maintaining blood glucose within normal limits is essential. Regular blood glucose monitoring and following the diet and medication prescribed by your doctor are key to diabetes control.
Daily examination of the feet: A careful examination of the feet daily can quickly identify any skin changes, swelling or sores. Any changes should be reported to the doctor immediately.
- Cause: Neglected sores or irritations can quickly progress into serious infections.
- Solution: Check feet daily for signs of sores, swelling, discoloration or skin changes. Report any changes to your doctor immediately.
Proper hygiene: Wash feet thoroughly, paying particular attention to the areas between the toes. After washing, dry feet thoroughly and apply a moisturiser, avoiding excess moisture.
- Cause: Dry skin and unkempt nails can create minor cracks and sores, which can become entry points for infection.
- Solution: Keep your feet’s skin moisturised, avoid excessive nail trimming and groom them regularly. Avoid shoes that are tight or cause pressure on the toes.
Choosing the Right Footwear: Wear comfortable shoes with rounded toes and check the inside of the shoe to prevent rubbing or excessive pressure.
- Cause: Inappropriate footwear can cause sores, calluses, and foot deformities.
- Solution: Choose comfortable, round-toed footwear with no inside seams or objects that can irritate the skin. Try to avoid walking barefoot and protect your feet in environments with a high risk of injury.
Regular Doctor Visits: Schedule regular visits to the doctor to evaluate the condition of your feet and adjust your treatment plan if necessary.
- Cause: Lack of constant monitoring can lead to neglect of foot problems.
- Solution: Schedule regular visits to the doctor to assess feet and adjust treatment plan if necessary. Don’t hesitate to seek medical help immediately if you notice any significant changes.
Prompt Wound Treatment: Any injury, even seemingly minor ones, should be treated immediately to prevent infection and ensure proper healing. Careful cleaning of the wound, application of a sterile dressing and regular monitoring of the progress are essential steps. It is crucial to seek medical attention for wounds that do not heal properly or become inflamed.
- Cause: Untreated wounds can quickly develop into infections, increasing the risk of complications.
- The solution: All wounds, even small ones, should be treated promptly. Proper hygiene and the use of sterile bandages can help prevent infection.
Promoting Blood Circulation: Poor blood circulation can slow the healing process and increase vulnerability to problems such as wounds and ulcers. To improve circulation, adopting a healthy lifestyle is essential, including regular exercise and avoiding habits such as smoking. Controlling blood pressure and managing body weight also contributes to maintaining optimal blood circulation. Consultation with your doctor for personalised advice based on your individual health is recommended.
- Cause: Poor blood circulation can delay wound healing and promote problems.
- Solution: Adopt a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, avoidance of smoking and control of blood pressure to improve blood circulation.
Don’t hesitate to seek your doctor’s advice to tailor your care plan to your specific needs and conditions.
Conclusion
The diabetic foot should not be underestimated, and a proactive attitude can make all the difference in preventing severe complications. The prevention and care of diabetic foot requires close collaboration with the medical team so that any problems are identified and treated at an early stage. Constant monitoring, proper care and regular medical consultation can help maintain foot health and avoid more serious problems associated with the condition.
It is essential to seek medical attention when you notice any change in the colour of the skin of your feet or other symptoms related to diabetic foot.
For more information or if you would like a consultation, please do not hesitate to contact us.